Manual pumps are essential tools for extracting water from wells, offering a reliable, energy-efficient, and cost-effective solution. These pumps are ideal for households and communities seeking sustainable water access, especially in areas with limited electricity. They empower users to manage their water supply independently, ensuring consistency and reducing dependence on external factors. Designed for durability and ease of use, manual pumps require minimal maintenance and provide a long-lasting solution for water extraction needs. Their simplicity and effectiveness make them a cornerstone of self-sufficient living and sustainable practices.
1.1 What is a Manual Pump?
A manual pump is a water extraction device powered solely by human effort, typically through hand or foot operation. It is designed to draw water from wells, cisterns, or other water sources without the need for electricity or external energy. Operations involve pushing, pulling, or pressing mechanisms to move water from the source to the surface. These pumps come in various designs, such as hand pumps, lever pumps, and piston pumps, each suited to specific water extraction needs. Manual pumps are widely used in rural and off-grid settings due to their simplicity, portability, and low operational costs. They rely on basic mechanical principles to function efficiently, making them a reliable choice for communities with limited resources.
1.2 The Importance of Manual Pumps in Water Extraction
A manual pump plays a crucial role in several key areas:
Energy Independence: They function without external power, making them ideal for rural or remote areas with limited electricity access.
Cost-Effectiveness: Lower operational costs as they don’t require electricity or fuel, suiting tight budgets for communities;
Reliability in Emergencies: Essential during power outages, ensuring a continuous water supply when other pumps fail.
Durability and Longevity: Easy maintenance with fewer parts, allowing them to serve communities for years with proper care.
Portability and Flexibility: Easily movable between wells or locations, adapting to various water source needs.
Disaster Response: Quickly deployable in emergencies for clean water access when other systems are compromised.
Empowerment: Provides communities with self-reliance, reducing dependence on external resources like electricity or fuel.
These attributes underscore the vital role of manual pumps in ensuring sustainable and reliable water extraction in challenging conditions.
1.3 Benefits of Using a Manual Pump for Wells
Manual pumps offer several advantages in the context of water extraction from wells:
- Affordability: They have low upfront costs and require minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective option, especially for those with limited resources.
- Environmental Friendliness: As they do not consume electricity, manual pumps contribute to energy conservation and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with eco-friendly practices.
- Practicality in Remote Areas: Ideal for regions without electricity, manual pumps provide a reliable water source without relying on external power grids.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: With fewer components, installation is straightforward, and repairs can often be done without specialized skills or tools.
- Empowerment and Independence: Users gain self-reliance, as manual pumps allow control over water supply, crucial during emergencies when other systems may fail.
- Durability: Fewer moving parts mean increased longevity, offering a sustainable long-term solution with reduced need for frequent replacements.
- Portability: Manual pumps are often compact and lightweight, allowing easy movement and installation in various locations as needed.
- Promotion of Water Conservation: The physical effort required to pump water may encourage mindful usage, fostering better conservation habits.
- Health and Safety: Easy to clean and maintain, manual pumps can reduce the risk of contamination, ensuring a safer water supply.
Overall, manual pumps provide a practical, sustainable, and cost-effective solution for water extraction, benefiting many communities and individuals.
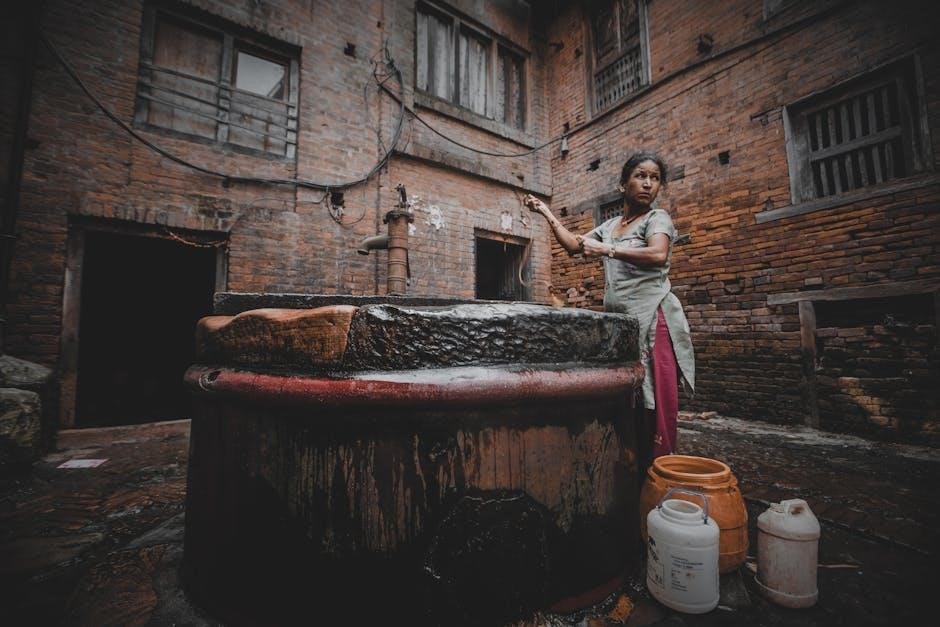

Types of Manual Pumps for Wells
Manual pumps for wells include lever, piston, hand, and submersible pumps. Each type caters to different depths, volumes, and environmental conditions, providing reliable and efficient water extraction solutions.
2.1 Lever Pump
Lever pumps use a long handle and leverage to lift water from the well, reducing manual effort. The user pulls the lever, which operates a piston inside the pump, creating suction to draw water upward. These pumps are ideal for shallow wells and temporary water extraction, offering easy operation and durability. The lever mechanism ensures consistent water flow with minimal physical strain, making them a practical choice for remote or low-power environments.
Lever pumps rely on a mechanical advantage to lift water, minimizing the force needed for operation. The lever’s length allows users to pull water to the surface efficiently, even from moderate depths. Designed for simplicity, these pumps are easy to maintain and operate, making them a reliable option for rural or off-grid water systems. Their compact design and portability enhance their versatility in various settings.
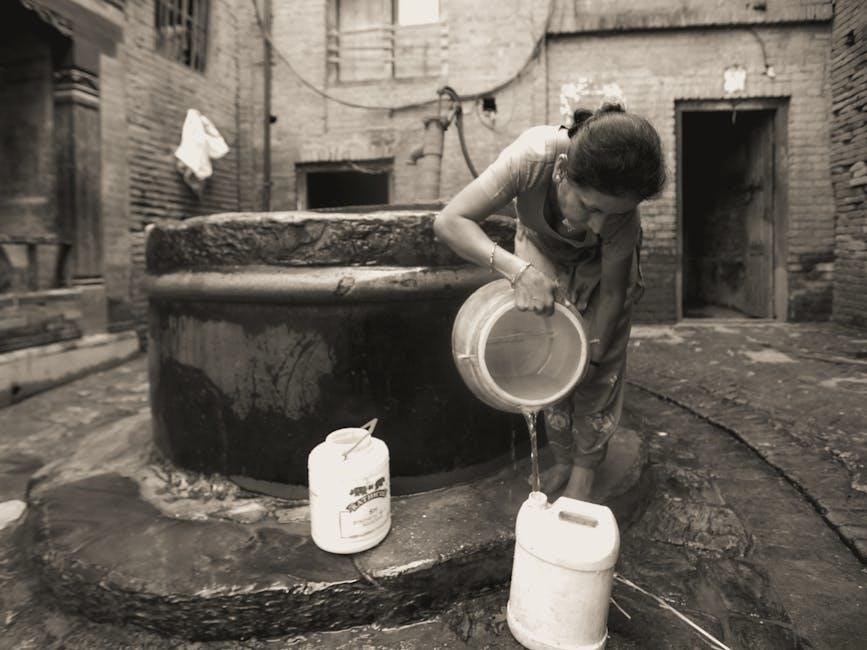

Lever pumps are mechanical devices that use leverage to extract water from wells. By pulling a long handle, users activate a piston or plunger, creating suction that draws water upward through the pump’s body. These pumps are typically installed above ground, connected to a cylinder or pipe extending into the well. Lever pumps are known for their simplicity, efficiency, and ability to provide consistent water flow, making them a popular choice for manual water extraction.
2.2 Piston Pump
Piston pumps are highly efficient manual water extraction devices that utilize a reciprocating piston to draw water from the well. The piston moves up and down inside a cylinder, creating a vacuum that lifts water to the surface through a check valve system. This mechanism ensures a consistent and strong water flow, making piston pumps ideal for deeper wells. The pump’s durability and minimal maintenance requirements contribute to its reliability, while its versatility accommodates various well depths and water volume demands. With proper care, piston pumps can provide years of dependable service, enhancing water access in both rural and urban settings. Their efficiency and robust design make them a top choice for manual well pumping systems.
2.3 Hand Pump
Hand pumps are simple, manually operated devices designed for extracting water from shallow wells. They are easy to install and require minimal effort to operate, making them ideal for households and small communities. Unlike piston pumps, hand pumps use a lever or handle system to Drawing water, providing a convenient and low-maintenance option for water extraction.
Hand pumps are lightweight and portable, making them a cost-effective solution for temporary or emergency water needs. They are commonly used in rural areas where electricity is unavailable. Regular use of a hand pump ensures consistent water supply while minimizing downtime. Their adaptability and ease of operation make them a practical choice for sustainable water management systems.
2.4 Hand-Operated Submersible Pump
Hand-operated submersible pumps are designed to draw water from deep wells and are submerged inside the water source for efficient operation. These pumps feature a long handle, allowing users to pull water up manually. They are highly portable and can be easily moved between locations, making them ideal for temporary or remote well setups.
Unlike traditional hand pumps, submersible models prevent sediment and debris from entering the pump, ensuring cleaner water extraction. Their compact design and ease of use make them suitable for small-scale water needs, especially in areas with limited infrastructure. Regular use and proper maintenance ensure reliable performance for years to come.
These pumps are also excellent for preventing well erosion, as they minimize water turbulence during operation. Their robust construction and durability make them a practical choice for various environments. Homeowners and professionals rely on hand-operated submersible pumps for their efficiency and adaptability in water management.

How to Choose the Right Manual Pump for Your Well
Choosing the right manual pump involves evaluating well depth, water volume, material durability, ease of use, maintenance needs, and personal preferences to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
3.1 Factors to Consider When Selecting a Manual Pump
Choosing the right manual pump involves evaluating several key factors. First, consider the pump’s intended use, whether for drinking water, irrigation, or other purposes. Next, assess the depth of your well and the desired water flow rate. Durability and materials are crucial, as the pump should withstand regular use and harsh outdoor conditions. Additionally, ease of operation and maintenance must be prioritized, along with budget and space requirements. These factors ensure the pump meets your needs effectively and efficiently.
3.2 Compatibility with Well Depth and Water Volume
When selecting a manual pump, ensuring compatibility with well depth and water volume is critical for optimal performance. Pumps designed for shallow wells may struggle to extract water from deeper sources, while those meant for deep wells may be too powerful or difficult to operate in shallow settings. The water volume required also influences pump selection—higher flow rates are needed for irrigation or multiple household uses. Always verify the pump’s capacity against your well’s characteristics to ensure reliable and efficient water extraction without overcomplicating the system. Proper alignment of pump specs with well conditions guarantees long-term functionality and minimizes maintenance issues.
3.3 Material and Durability of the Pump
Material and Durability of the Pump
Choosing the right material for your manual pump is crucial for ensuring durability and longevity. Pumps made from high-quality, rust-resistant metals or durable plastics are ideal, as they can withstand regular use and harsh conditions. Consider factors like corrosion resistance, weight, and strength when selecting materials. Durable materials reduce wear and tear, making the pump more reliable over time. Additionally, proper construction techniques and high-quality components enhance the pump’s ability to handle various water extraction demands. Investing in a pump with robust materials ensures efficient performance and reduces the likelihood of costly repairs. .

Installation of a Manual Pump
Manual pump installation requires careful preparation and precise execution. Proper alignment and sealing are crucial to ensure efficient operation and prevent leaks. Follow manufacturer guidelines to select the right materials and tools for a durable setup. A correctly installed pump ensures reliable water extraction and long-term performance. Proper installation minimizes issues and Maximizes pump longevity. .
4.1 Preparing the Well for Pump Installation
Before installing a manual pump, it is crucial to prepare the well properly. Start by cleaning the well shaft to ensure there is no debris or contamination. Inspect the sides for damage or irregularities that could interfere with the pump’s operation. Ensure the wellhead is secure and level to provide a stable foundation for the pump. Remove any accumulated sediment or rust to enhance longevity. Proper preparation also involves ensuring the surface area around the well is clear and easily accessible. Regular cleaning and maintenance will help maintain water quality and pump efficiency. If necessary, install a cover or screen to prevententry. Effective preparation ensures smooth installation and optimal performance of the manual pump. Proper alignment and sealing are essential for leak-proof operation. By preparing the well thoroughly, you ensure the pump functions reliably and efficiently for years to come. Always follow safety guidelines and use appropriate tools during the preparation process. This step is vital for a successful and long-lasting pump installation.
4.2 Step-by-Step Installation Process
To install a manual pump for your well, begin by assembling the pump components according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Position the pump near the wellhead and ensure it is level. Attach the suction and discharge pipes securely. Lower the pump into the well carefully, using a winch or pulley if necessary. Once in place, connect the pump to the well casing, ensuring proper alignment and sealing to prevent leaks. Anchor the pump firmly to the ground and connect the handle or lever. Prime the pump by pouring water into the priming cup or pouring water into the discharge pipe to ensure smooth operation. Test the pump by manually operating the handle, checking for leaks and proper water flow. Adjustments may be needed for optimal performance. Finally, secure all connections and clean the area around the pump for a neat and functional setup.
4.3 Ensuring Proper Alignment and Sealing
Proper alignment is critical for optimal performance and longevity of your manual pump. Ensure the pump is straight and aligned with the well casing to prevent misoperation or wear. Check the pump body and casing for straightness before installation. Use a level or alignment tool to verify correct positioning. Tighten all connections securely to prevent leaks. For sealing, use high-quality gaskets or O-rings to create a watertight connection. Regularly inspect joints and tighten as needed to maintain efficiency and prevent contamination. Proper alignment and sealing ensure smooth operation and minimize the risk of mechanical failure.

Maintenance and Care for Manual Pumps
Routine maintenance is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of manual pumps. Regularly inspect the pump mechanism, clean it, and lubricate moving parts as needed. Addressing issues promptly ensures reliable operation and prevents costly repairs. Proper care guarantees consistent water flow and prevents contamination, safeguarding your water supply.
5.1 Routine Maintenance Tips
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the pump after each use with mild soap and water to prevent dirt buildup and contamination.
- Inspect for Wear: Check for cracks, loose parts, or wear on moving components, and address issues promptly to prevent breakdowns.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply a suitable lubricant to ensure smooth operation and reduce friction in the pump mechanism;
- Check Alignment: Ensure the pump is properly aligned to maintain efficiency and prevent strain on components.
- Tighten Connections: Regularly inspect and tighten bolts and connections to prevent leaks and ensure secure operation.
- Dry Storage: Store the pump in a dry place to avoid rust or mold when not in use.
- Monitor Performance: Address any unusual noises or reduced efficiency by performing a thorough inspection;
- Replace Worn Parts: Promptly replace damaged valves, seals, or other parts to maintain functionality and water flow.
Regular maintenance ensures the pump operates efficiently, prevents long-term damage, and maintains consistent water flow. Always prioritize safety when handling the pump and its components.
5.2 Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Contamination: Regularly clean the pump and store water in food-grade containers to prevent contamination. Sanitize weekly to maintain water quality.
- Wear and Tear: Inspect for worn parts and replace them promptly. Damage to valves or seals can affect performance and must be addressed.
- Misalignment: Ensure proper alignment to prevent inefficiency and wear. Misalignment can reduce water flow and increase pumping difficulty.
- Leaks: Tighten connections and inspect for leaks. Loose bolts or damaged seals can lead to leaks, so repairs should be made promptly.
- Difficult Pumping: Check for blockages or pressure issues. Clean the pump and operate within its limits, lubricating parts if necessary.
Regular checks and prompt repairs ensure efficient operation, reliable water access, and extended pump lifespan.
5.3 Cleaning and Sanitizing the Pump
- Disassembly and Cleaning: Begin by disassembling the pump. Use mild detergents and soft brushes to clean each part, ensuring all components are free from debris and buildup.
- Sanitization: Apply a food-safe sanitizing solution, ensuring all parts are thoroughly soaked. Rinse with clean water and allow to dry completely before reassembly to prevent contamination.
- Storage: Store disassembled parts in food-grade containers to protect them from dust and moisture, ensuring they are ready for the next use while maintaining hygiene.
Benefits of Using a Manual Pump for Wells
Manual pumps offer independence from electricity, empowering users to manage water supply consistently. They ensure a reliable and sustainable source, reducing reliance on external factors while maintaining hygiene and efficiency.
6.1 Cost-Effectiveness
Manual pumps are a cost-effective solution for well water extraction, requiring minimal initial investment compared to motorized alternatives. They have low operating costs, as they rely on manual operation rather than electricity. Over time, their durability and low maintenance requirements make them a financially sustainable choice for long-term use. Additionally, they eliminate the need for expensive energy supplies, further reducing overall costs. This makes manual pumps an ideal option for budget-conscious users
6.2 Low Maintenance Requirements
Manual pumps require minimal upkeep, making them an ideal choice for well water extraction. Their simple design reduces the need for frequent repairs or professional servicing. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and inspecting parts, ensures longevity and optimal performance. With little to no advanced technical knowledge needed, users can easily maintain these pumps. This low-maintenance feature makes manual pumps a reliable and hassle-free solution for consistent water supply. Their durability and ease of use ensure minimal intervention, further enhancing their practicality.
6;3 Reliability During Power Outages
Manual pumps provide unparalleled reliability during power outages, ensuring continuous water access. Unlike electrified systems, they function without electricity, making them a dependable backup for emergencies. Whether due to storms, grid failures, or remote locations, manual pumps remain operational, avoiding supply disruptions. Their independence from power ensures that water extraction remains feasible, even in challenging conditions. This makes manual pumps an ideal choice for maintaining water accessibility during unexpected outages.

Challenges and Limitations of Manual Pumps
Manual pumps require physical effort, which can lead to fatigue. They also have slower water extraction rates compared to motorized systems. Additionally, they may need frequent maintenance to function properly over time.
7.1 Physical Strain During Operation
Operating a manual pump requires physical effort, especially when extracting water from deep wells or under high demand. Repeated use can lead to muscle fatigue, discomfort, or strain, particularly without proper technique or rest. Users may find it challenging to maintain consistent performance, especially in areas with limited access to alternative systems. While manual pumps are cost-effective, the physical demands make them less suitable for continuous or large-scale water extraction. Always ensure regular breaks and proper form to minimize strain and maximize efficiency.
7.2 Limited Water Extraction Speed
Manual pumps, while reliable and simple, have notable limitations regarding their extraction speed. Their dependence on manual labor inherently reduces the rate at which water can be retrieved, making them less efficient for large-scale or high-demand scenarios. This limitation is particularly evident in deep wells or areas with low water levels, where the extraction process becomes slower and more labor-intensive.
Consistency in water supply is another challenge. Variations in human effort can cause fluctuations in water flow, which may disrupt activities requiring a steady water supply, such as cooking or irrigation. The slower extraction speed also poses issues during emergencies or peak usage times, potentially leading to delays or shortages.
Despite these drawbacks, solutions exist. Utilizing multiple manual pumps or integrating them with alternate power sources can enhance extraction efficiency. Additionally, regular maintenance ensures the pump operates at its maximum potential, albeit still slower than motorized alternatives. Users must weigh these limitations against the pump’s advantages, such as low maintenance and energy independence, to determine if a manual pump suits their needs.
7.3 Dependence on Regular Maintenance
Manual pumps for wells require consistent and regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Despite being reliable, these pumps are susceptible to wear and tear due to exposure to outdoor elements and frequent use. Regular upkeep involves routine cleaning to prevent dirt buildup, inspecting for any signs of damage or wear, tightening loose components, and applying lubrication to moving parts. Neglecting maintenance can lead to inefficiencies, such as reduced water extraction efficiency or potential malfunctions, which can disrupt water supply reliability. To prevent these issues, it is advisable to schedule maintenance periodically, whether weekly or monthly, depending on usage frequency. Following manufacturer guidelines or seeking advice from community resources or local experts can provide additional insights into best practices for maintaining manual pumps. Additionally, timely replacement of worn-out parts, such as washers or gaskets, is essential to prevent leaks and maintain efficiency. By prioritizing regular maintenance, users can ensure their manual pumps remain functional and reliable, which is crucial in areas where access to clean water is vital.

Comparing Manual Pumps with Other Water Extraction Methods
Manual pumps offer a reliable, low-maintenance alternative to motorized pumps, ideal for remote areas with limited electricity. Unlike hand-dug wells, they provide controlled water flow and easier extraction; Their portability and cost-effectiveness make them a practicalchoice for sustainable water access.
8.1 Manual vs. Motorized Pumps
Manual pumps rely on physical effort to draw water, making them ideal for low-power settings. They are durable, portable, and require minimal maintenance. In contrast, motorized pumps use electricity orengine power for faster and higher-volume extraction. While manual pumps are cost-effective and eco-friendly, motorized pumps offer convenience and efficiency. However, they depend on external power and can be more complex to maintain.
8.2 Manual Pumps vs. Hand-Dug Wells
Manual pumps provide a reliable, mechanical method for water extraction, while hand-dug wells rely on manual labor to access groundwater. Manual pumps are faster and more efficient, reducing the time spent fetching water. Hand-dug wells, however, require physical digging and are dependent on seasonal water levels. Pumps offer year-round reliability, even during dry spells, whereas wells may dry up. Manual pumps also eliminate the need for constant digging and cleaning, making them more sustainable in the long term. Both methods have their challenges, but pumps offer greater ease and consistency in water access.

Manual pumps remain a reliable and sustainable solution for water extraction, especially in areas with limited resources. They offer cost-effectiveness, low maintenance, and independence from external power sources. By empowering individuals to manage their water supply, manual pumps promote self-sufficiency and resilience, particularly during power outages or emergencies. Regular maintenance ensures longevity and optimal performance, while proper selection and installation guarantee efficiency. With advancements in design, manual pumps continue to be a practical choice for communities worldwide. Remember, clean and safe storage of water is equally important—use solid, food-grade buckets as recommended online to maintain water quality and hygiene.




